Abstract
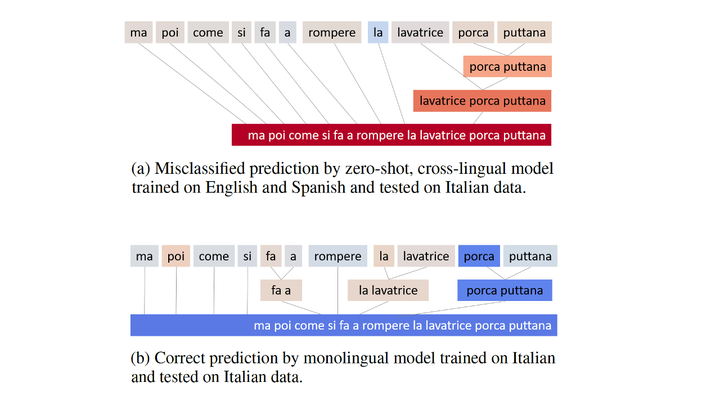
Reducing and counter-acting hate speech on Social Media is a significant concern. Most of the proposed automatic methods are conducted exclusively on English and very few consistently labeled, non-English resources have been proposed. Learning to detect hate speech on English and transferring to unseen languages seems an immediate solution. This work is the first to shed light on the limits of this zero-shot, cross-lingual transfer learning framework for hate speech detection. We use benchmark data sets in English, Italian, and Spanish to detect hate speech towards immigrants and women. Investigating post-hoc explanations of the model, we discover that non-hateful, language-specific taboo interjections are misinterpreted as signals of hate speech. Our findings demonstrate that zero-shot, cross-lingual models cannot be used as they are, but need to be carefully designed.